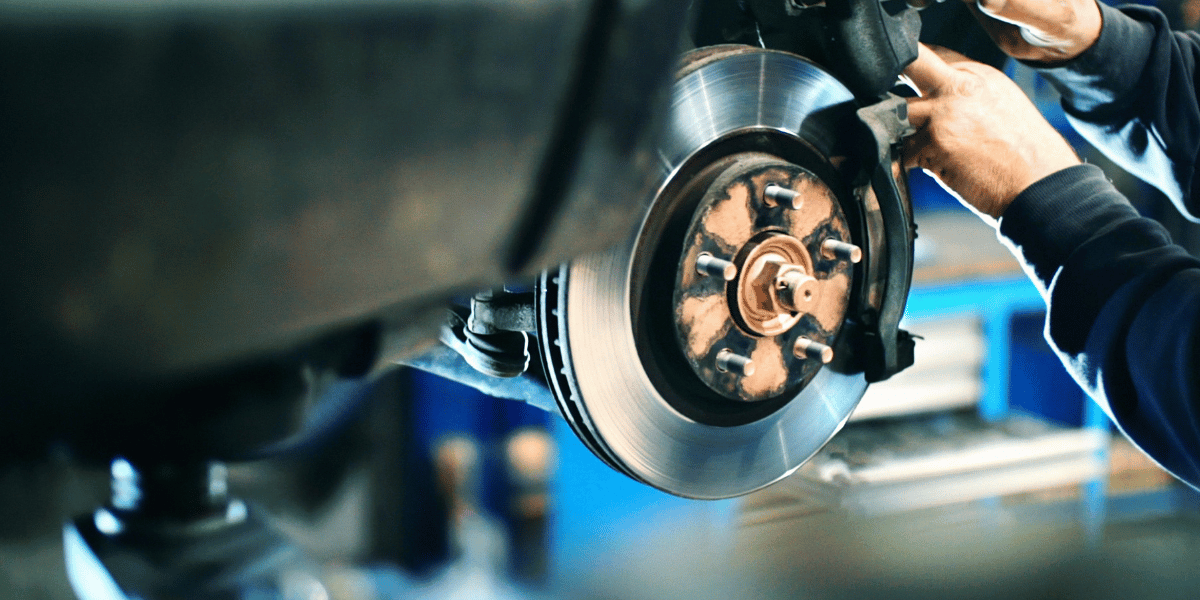
When it comes to driving, safety should always be a top priority. One technique that can make a big difference in emergency situations is brake boosting. But what exactly is brake boosting, and how can you use it safely and effectively?
Brake boosting is a technique that uses the engine’s power to increase the braking force of a vehicle. It is done by pressing the brake pedal and accelerator pedal at the same time. Brake boosting is most effective on turbocharged or supercharged cars, as these cars have more power available at low RPM. However, brake boosting can also be used on naturally aspirated cars.
How it Works:
To understand brake boosting, you first need to grasp the basics of your vehicle’s braking system. Most modern cars are equipped with hydraulic brake systems, which use brake fluid to transmit force from the brake pedal to the brake calipers, causing the brake pads to squeeze the brake rotors and bring the vehicle to a halt.
Now, here’s where brake boosters come into play: These nifty components are designed to amplify the force you apply to the brake pedal, making it easier to slow down or stop your vehicle. There are four main types, each with its unique characteristics:
- Hydraulic: These older-style boosters utilize hydraulic pressure from the power steering system to assist in braking. They’re commonly found in older vehicles and some heavy-duty applications.
- Vacuum: Most modern passenger vehicles use vacuum brake boosters, which harness engine vacuum to aid in braking. They are known for their efficiency and responsiveness.
- Electronic: The latest addition to the brake booster family, electronic boosters, employ electronic sensors and actuators to assist in braking. They offer precise control but are less common.
- Mechanical: Mechanical brake boosters are relatively rare and rely on mechanical linkages to amplify the force applied to the brake pedal. You might find them in vintage vehicles.
Dangers of Brake Boosting:
While brake boosting can be a valuable skill, it’s essential to be aware of the potential risks associated with it. Here are some of the dangers to keep in mind:
- Overheating Brake Components: Excessive brake boosting can lead to the overheating of brake components, such as brake pads and rotors. This can reduce braking effectiveness and cause premature wear.
- Brake Fade: Brake fade occurs when prolonged heavy braking causes a loss of friction between the brake pads and rotors. This can result in a significant reduction in stopping power.
- Reduced Brake Pad and Rotor Lifespan: Continuous aggressive brake boosting can significantly shorten the lifespan of your brake pads and rotors, potentially leading to costly replacements.
- Loss of Control: Rapid and aggressive brake boosting can upset the balance of your vehicle, increasing the risk of a loss of control, especially on slippery surfaces.
- Increased Stopping Distance: Ironically, improper brake boosting techniques can increase stopping distances, which can be dangerous in emergency situations.
When to Use:
Now that we’ve covered the potential dangers, let’s talk about when it’s appropriate to use. Here are some scenarios where brake boosting can be beneficial:
- Emergency Situations: Brake boosting is most commonly employed in emergency situations when you need to bring your vehicle to a sudden stop to avoid a collision.
- Hill Descents: When navigating steep descents, brake boosting can help control your speed and prevent your vehicle from gaining excessive momentum.
- Towing Heavy Loads: If you’re towing a heavy trailer or carrying a substantial load, brake boosting can provide the extra stopping power needed to bring the added weight to a halt safely.
- Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) Activation: In certain situations, your vehicle’s ABS system may activate. Brake boosting can complement the ABS system’s efforts to bring your vehicle to a stop while maintaining steering control.
How to do Safely:
Safety should always come first when using brake boost. To ensure you use this technique responsibly, follow these tips for safety:
- Apply Steady Pressure: Instead of slamming on the brake pedal, apply steady and progressive pressure. This allows your vehicle’s weight to transfer forward gradually, maximizing traction.
- Avoid Rapid Pumping: Resist the urge to rapidly pump the brakes, as this can lead to brake fade. Maintain constant pressure to optimize braking efficiency.
- Maintain Steering Control: While braking, keep a firm grip on the steering wheel and avoid sudden or jerky movements, as these can lead to a loss of control.
- Consider Road Conditions: Be mindful of road conditions, especially in adverse weather. Brake boosting on slippery surfaces can result in skidding, so adjust your technique accordingly.
- Know Your Vehicle’s Limitations: Different vehicles have varying braking capabilities. Understand your vehicle’s limitations and adjust your braking technique accordingly.
Signs & Symptoms:
Regular inspection of your vehicle’s braking system is essential to ensure it functions correctly, particularly if you frequently use brake boosting. Here are some signs that may indicate an issues:
- Spongy Brake Pedal: If your brake pedal feels spongy or soft, it could signal air in the brake lines or a brake fluid leak, both of which can be worsened by aggressive braking.
- Brake Warning Lights: Any illuminated brake warning lights on your dashboard should be investigated promptly to avoid potential brake problems.
- Increased Braking Distance: If you notice that your vehicle’s stopping distance has increased significantly, it could be due to brake pad or rotor wear, which can be accelerated by brake boosting.
- Unusual Noises: Strange noises, such as squealing or grinding, when you brake can be indicative of brake pad or rotor issues caused by aggressive braking.
- Brake Fluid Leaks: Keep an eye out for any signs of brake fluid leaks, as these can compromise the effectiveness of your brakes, especially under heavy use.
Can I rebuild my brake booster?
Your brake booster is a critical component of your vehicle’s braking system. It uses engine vacuum to amplify the force of your foot on the brake pedal, making it easier to stop your car.
Over time, brake boosters can wear out and fail. This can be caused by a number of factors, including age, mileage, and environmental conditions.
If your brake booster fails, you will notice a significant decrease in braking power. You may also have to press the brake pedal much harder than usual to stop your car.
In some cases, it may be possible to rebuild. This is a complex process that requires specialized tools and knowledge. If you are not comfortable rebuilding by yourself, you should take it to a qualified mechanic.
Here are some of the pros and cons of rebuilding:
Pros:
- Rebuilding brake booster can save you money compared to buying a new one.
- It can also be a more environmentally friendly option, as it reduces the amount of waste that goes to landfills.
Cons:
- Rebuilding brake booster is a complex process that can be difficult and time-consuming.
- If not done properly, it can compromise the safety of your vehicle’s braking system.
If you decide to rebuild your by yourself, here are some things to keep in mind:
- Make sure you have the correct tools and knowledge. There are many tutorials available online and in automotive repair manuals.
- Be careful not to damage any of the components during disassembly and reassembly.
- Use only high-quality replacement parts.
- Once you have rebuilt your brake booster, be sure to test it thoroughly before driving your car.
Here are some signs that your brake booster may need to be rebuilt or replaced:
- Hard brake pedal: If you have to press the brake pedal much harder than usual to stop your car, this could be a sign of a failing brake booster.
- Soft brake pedal: If the brake pedal feels soft or spongy, this could also be a sign of a failing brake booster.
- Increased stopping distance: If it takes longer than usual to stop your car, this could be a sign of a failing brake booster.
- Hissing noise: If you hear a hissing noise when you press the brake pedal, this could be a sign of a leak in the brake booster.
Conclusion
Whether or not you should rebuild your brake booster depends on a number of factors, including your skill level, the availability of parts, and the cost of a replacement booster. If you are unsure whether or not you can rebuild by yourself, it is always best to consult with a qualified mechanic.
APR Brake Boosting Technique
APR brake boosting is a technique that can be used to improve the acceleration of turbocharged vehicles. It involves applying the brake and accelerator pedals simultaneously, which forces the turbocharger to spool up more quickly. This can result in a significant increase in boost pressure, which can translate into faster acceleration.
How to do?
Follow these steps:
- Get your vehicle up to a speed of at least 20 mph.
- Apply pressure to the brake pedal with your left foot.
- While still pressing the brake pedal, slowly depress the accelerator pedal with your right foot.
- Continue to apply pressure to both pedals until you reach the desired boost pressure.
- Once you have reached the desired boost pressure, release the brake pedal and accelerate.
Pros
There are several benefits to brake boosting, including:
- Increased acceleration: Brake boosting can significantly improve the acceleration of turbocharged vehicles. This can be especially beneficial in roll races or when launching from a stop.
- Improved handling: Brake boosting can also help to improve the handling of turbocharged vehicles by reducing turbo lag. This can make the vehicle more responsive and easier to control.
- Increased fuel efficiency: Brake boosting can also help to improve the fuel efficiency of turbocharged vehicles by reducing the amount of time that the engine needs to run at high boost levels.
Cons
While there are several benefits to brake boosting, there are also some drawbacks to consider, including:
- Increased wear on the brakes: Brake boosting can increase wear on the brake pads and rotors. This is because brake boosting requires you to apply pressure to the brake pedal while simultaneously applying the accelerator pedal.
- Increased wear on the engine: Brake boosting can also increase wear on the engine. This is because brake boosting can cause the engine to run at high boost levels for extended periods of time.
- Increased risk of wheel spin: Brake boosting can increase the risk of wheel spin, especially in wet or slippery conditions.
Overall, APR brake boosting is a technique that can be used to improve the acceleration and handling of turbocharged vehicles. However, it is important to be aware of the potential drawbacks before using this technique.
Electronic brake boosting (E-Booster): What it is and how it works
E-Booster is a technology that uses an electric motor to amplify the driver’s brake pedal force. This can provide a number of benefits, including:
- Reduced driver fatigue: E-Boosters can make it easier to brake, especially in hard braking situations or when towing a trailer.
- Improved braking performance: E-Boosters can provide more consistent braking performance, even under varying conditions such as engine temperature or load.
- Reduced brake pedal travel: E-Boosters can reduce the distance that the driver needs to press the brake pedal before the brakes are applied.
- Enhanced safety features: E-Boosters can be used to implement advanced safety features such as automatic emergency braking (AEB).
How does E-Booster Work?
An E-Booster system typically consists of the following components:
- Brake pedal sensor: This sensor detects the position of the brake pedal and sends a signal to the electronic control unit (ECU).
- ECU: The ECU is the brain of the E-Booster system. It receives signals from the brake pedal sensor and other sensors, such as the wheel speed sensors. The ECU then calculates how much brake boost to provide and sends a signal to the electric motor.
- Electric motor: The electric motor is used to amplify the driver’s brake pedal force. It is connected to the brake master cylinder through a mechanical linkage.
When the driver presses the brake pedal, the brake pedal sensor sends a signal to the ECU. The ECU then calculates how much brake boost to provide and sends a signal to the electric motor. The electric motor then turns on and applies additional force to the brake master cylinder. This additional force is used to amplify the driver’s brake pedal force and apply the brakes more effectively.
Benefits
E-Boosters offer a number of benefits over traditional vacuum brake boosters, including:
- Improved braking performance: E-Boosters can provide more consistent braking performance, even under varying conditions such as engine temperature or load. This is because E-Boosters are not dependent on the engine vacuum, which can fluctuate depending on engine speed and load.
- Reduced brake pedal travel: E-Boosters can reduce the distance that the driver needs to press the brake pedal before the brakes are applied. This can make braking easier and faster, especially in emergency situations.
- Enhanced safety features: E-Boosters can be used to implement advanced safety features such as automatic emergency braking (AEB). AEB systems can automatically apply the brakes if the vehicle is about to collide with another vehicle or object.
Applications of E-Booster
E-Boosters are used in a wide variety of vehicles, including cars, SUVs, trucks, and buses. They are especially popular in hybrid and electric vehicles, as these vehicles do not have an engine vacuum to power a traditional vacuum brake booster.
Conclusion: E-Booster is a technology that offers a number of benefits over traditional vacuum brake boosters. It can improve braking performance, reduce brake pedal travel, and enable advanced safety features. E-Boosters are used in a wide variety of vehicles, including cars, SUVs, trucks, and buses.
Hydraulic Boosting
Hydraulic brake boosters are used to amplify the force applied to the brake pedal, resulting in more powerful braking. This is especially important in heavy-duty vehicles and vehicles with large brakes, which require more force to stop effectively.
Hydraulic brake boosters work by using a hydraulic pump to generate high-pressure fluid. This fluid is then used to push a piston, which in turn amplifies the force applied to the brake pedal.
There are two main types:
- Integral hydraulic: These boosters are integrated into the master cylinder and are typically used in light-duty vehicles.
- Remote hydraulic: These boosters are mounted separately from the master cylinder and are typically used in heavy-duty vehicles.
There are number of advantages over other types of brake boosters, such as:
- More powerful braking: Hydraulic brake boosters can provide more powerful braking than other types of boosters, such as vacuum boosters. This is because hydraulic boosters can generate more force.
- Faster response time: Hydraulic brake boosters have a faster response time than other types of boosters. This is because the hydraulic fluid is able to travel very quickly through the system.
- More reliable: Hydraulic brake boosters are more reliable than other types of boosters, such as vacuum boosters. This is because hydraulic boosters are not susceptible to vacuum leaks.
Hydraulic brake boosters are used in a variety of vehicles, including:
- Cars
- Trucks
- SUVs
- Buses
- Vans
- Heavy-duty vehicles
- Bulldozers, excavators, and loaders.
Hydraulic brake boosters are also used in some types of motorcycles and other two-wheeled vehicles.
Maintenance Tips
Hydraulic brake boosters are relatively low-maintenance, but there are a few things you can do to keep them in good working order:
- Check the hydraulic fluid level regularly and add fluid as needed.
- Inspect the hydraulic lines and hoses for leaks and damage.
- Have the hydraulic brake booster inspected and serviced by a qualified mechanic regularly.
Troubleshooting Problems
If you are experiencing problems with your hydraulic brakes, there are a few things you can check:
- Check the hydraulic fluid level. If the fluid level is low, add fluid as needed.
- Inspect the hydraulic lines and hoses for leaks and damage. If you find any leaks or damage, have the lines or hoses replaced.
- Check the hydraulic brake booster. If the booster is not working properly, it may need to be replaced.
Porsche Brake Boosting: Everything You Need to Know
Porsche brake boosting is a technique that can be used to improve the acceleration of Porsche turbocharged vehicles. It works by pre-loading the turbocharger with boost, which can then be released when the throttle pedal is pressed, resulting in a more immediate and powerful launch.
Brake boosting is a relatively simple technique, but it does require some practice to master. To brake boost, follow these steps:
- Come to a complete stop.
- Apply firm pressure to the brake pedal with your left foot.
- Press the throttle pedal with your right foot until the desired boost level is reached.
- Release the brake pedal and accelerate.
It is important to note that brake boosting can be dangerous if not done correctly. If too much boost is built up, the tires may break loose, causing the car to lose traction. It is also important to avoid revving the engine too high, as this can damage the turbocharger.
Advantages of Porsche brake boosting:
- Improved acceleration: Brake boosting can help Porsche turbocharged vehicles accelerate more quickly, especially from a standing start or from low speeds.
- Reduced turbo lag: Brake boosting can help to reduce turbo lag, which is the time it takes for the turbocharger to spool up and start producing boost.
- Better traction: Brake boosting can help to improve traction by pre-loading the tires with boost before the throttle pedal is pressed.
When to Use Porsche Technique:
- Drag racing: Brake boosting is a common technique used in drag racing to improve launch times.
- Rolling races: Brake boosting can also be used in rolling races to gain an advantage over your opponent.
- Autocross: Brake boosting can be used in autocross to launch the car out of corners more quickly.
- Overtaking: Brake boosting can be used to overtake other vehicles more safely and efficiently.
Conclusion
Porsche brake boosting is a powerful technique that can be used to improve the performance of Porsche turbocharged vehicles. However, it is important to use brake boosting safely and responsibly. If you are new to brake boosting, it is a good idea to practice in a safe area before using it on public roads.
Roll Racing Technique
Brake boosting is a technique used in roll racing to help turbocharged cars launch more quickly. It involves applying the brakes while simultaneously pressing on the accelerator pedal. This builds boost pressure in the turbocharger, which can then be used to propel the car forward when the brakes are released.
It is most effective at low speeds, when the turbocharger is not spinning as quickly. As the speed increases, the turbocharger will begin to spin more quickly and build boost pressure on its own. However, brake boosting can still be used to gain an advantage at higher speeds, especially if the turbocharger is relatively small.
Once you have built enough boost pressure, release the brakes and the car will launch forward. Be careful not to over-boost the turbocharger, as this can damage the engine.
Brake boosting is a powerful technique that can help you gain an advantage in roll racing. However, it is important to use it carefully, as it can damage the car if done incorrectly.
Here are some tips for brake boosting safely and effectively:
- Start by practicing brake boosting at low speeds. Once you have mastered the technique at low speeds, you can gradually increase the speed at which you practice.
- Be careful not to over-boost the turbocharger. Over-boosting can damage the engine.
- If you are unsure how much brake pressure to apply, start with a light touch and gradually increase the pressure until you build boost pressure.
- If the car starts to slow down too much, release the brakes and apply less pressure.
- Be aware of your surroundings and make sure there is enough room to brake boost safely.
Brake boosting is a fun and exciting technique that can help you improve your roll racing performance. However, it is important to use it safely and responsibly.
Brake Boosting vs Anti Lag
There are two different techniques used to improve the performance of turbocharged and supercharged engines.
Brake boosting is a technique that increases braking force by using the engine’s power. It is done by pressing the brake and accelerator pedals simultaneously. It is most effective on turbocharged or supercharged cars, but can also be used on naturally aspirated cars.
Anti-lag is a technique that keeps the turbocharger or supercharger spinning even when the throttle is closed. This is done by injecting fuel into the exhaust system, which is then ignited to create a small explosion that drives the turbine. Anti-lag can improve throttle response and reduce turbo lag, but it can also increase fuel consumption and emissions.
Here is a table comparing of brake boosting and anti-lag:
| Feature | Brake boosting | Anti-lag |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Increase braking force | Reduce turbo lag and improve throttle response |
| How it works | Uses engine power to assist in braking | Injects fuel into the exhaust system to keep the turbocharger or supercharger spinning |
| When to use it | In emergency situations, when towing a heavy load, or when descending a steep hill | When accelerating from a standstill or when shifting gears |
| Pros | Can significantly improve braking performance | Can improve throttle response and reduce turbo lag |
| Cons | Can overheat the brakes | Can increase fuel consumption and emissions |
| Vehicle compatibility | Can be used on all vehicles | Can only be used on turbocharged and supercharged vehicles |
Which one is better?
The best technique for you will depend on your individual needs and driving style. If you are looking for a way to improve your braking performance, then brake boosting is a good option. If you are looking for a way to reduce turbo lag and improve throttle response, then anti-lag is a good option.
It is important to note that both brake boosting and anti-lag can be dangerous if used incorrectly. It is important to practice these techniques in a safe environment before using them on the road.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is brake boosting?
A: Brake boosting is a technique used to increase the braking force of a vehicle by transferring weight to the front wheels. This is done by pressing the brake and accelerator pedals at the same time. Brake boosting is most effective on turbocharged or supercharged cars, as these cars have more power available at low RPM. However, brake boosting can also be used on naturally aspirated cars.
Q: Is brake boosting bad for your car?
A: Brake boosting is not bad for your car if done correctly. However, if you press the accelerator pedal too hard, you can damage your brakes or transmission. It is important to practice brake boosting in a safe area before using it in a real-world situation.
Q: Can you brake boost automatic?
A: Yes, you can brake boost an automatic car. However, it is important to be careful not to over-rev the engine. It is also a good idea to practice brake boosting in a safe area before using it in a real-world situation.
Q: Is brake boosting faster?
A: Yes, brake boosting can help you stop your car faster. However, it is important to note that brake boosting is not a substitute for good driving habits. Always be aware of your surroundings and drive defensively.
Q: Does brake boosting work?
A: Yes, brake boosting does work. It is a proven technique that can help you stop your car faster. However, it is important to practice brake boosting in a safe area before using it in a real-world situation.
Q: What does brake boosting do?
A: Brake boosting transfers weight to the front wheels of a vehicle. This increases the braking force and helps the car stop faster. Brake boosting is most effective on turbocharged or supercharged cars, as these cars have more power available at low RPM. However, brake boosting can also be used on naturally aspirated cars.
Q: Is brake boosting bad or hurt your car?
A: Brake boosting is not bad for your car if you done truly. However, if you press the accelerator pedal too hard, you can damage your brakes or transmission. It is important to practice brake boosting in a safe area before using it in a real-world situation.
Q: How does brake boosting work?
A: When you press the brake pedal, you are applying force to the brake calipers, which clamp down on the brake rotors. This slows the rotation of the wheels and helps the car stop. When you press the accelerator pedal, you are increasing the engine speed, which causes the wheels to rotate faster. This transfers weight to the front wheels, which increases the braking force.
Q: How bad is brake boosting?
A: Brake boosting is not bad for your car if done correctly. However, if you press the accelerator pedal too hard, you can damage your brakes or transmission. It is important to practice brake boosting in a safe area before using it in a real-world situation.
Q: What is brake boosting focus ST?
A: Brake boosting is a technique used to increase the braking force of a vehicle by transferring weight to the front wheels. This is done by pressing the brake and accelerator pedals at the same time. Brake boosting is most effective on turbocharged or supercharged cars, such as the Focus ST.
Q: Is brake boosting safe?
A: Brake boosting is a safe technique when done correctly. However, it is important to practice this technique in a safe area before using it in a real-world situation. You should also be aware of the risks involved, such as the possibility of wheel lockup.
Q: What is brake boosting turbo?
A: Brake boosting is a technique used to increase the braking force of a vehicle
Q: Can brake boosting damage my car?
A: Brake boosting itself, when done correctly and in moderation, is unlikely to cause significant damage to your car. However, aggressive and frequent brake boosting can accelerate wear and tear on your braking components, leading to premature maintenance or replacement.
Q: Is brake boosting the same as aggressive braking?
A: Brake boosting and aggressive braking are related but not the same. Brake boosting is a deliberate technique used to maximize stopping power, while aggressive braking refers to sudden and harsh braking actions. It’s possible to brake boost without being overly aggressive, but combining both can lead to more significant wear on your brakes.
Q: What is the difference between vacuum and hydraulic brake boosters?
A: Vacuum brake boosters use engine vacuum to assist in brake application, while hydraulic brake boosters rely on hydraulic pressure from the power steering system. Vacuum boosters are more common in modern vehicles due to their efficiency, but both types serve the same purpose of amplifying brake pedal force.
Q: Can I use brake boosting with ABS?
A: Yes, you can use brake boosting with vehicles equipped with Anti-lock Brake Systems (ABS). In fact, ABS systems are designed to work in conjunction with brake boosting techniques to maximize stopping power while maintaining steering control.
Q: How can I avoid overheating my brakes while brake boosting?
A: To prevent brake overheating, avoid prolonged and aggressive brake boosting. Apply steady and progressive pressure to the brake pedal, and if possible, downshift to use engine braking to assist in slowing down your vehicle.
Q: Are there any specific precautions for towing and brake boosting?
A: When towing heavy loads, brake boosting can be beneficial, but it’s essential to consider the added weight and adjust your braking technique accordingly. Give yourself more time and distance to slow down, and avoid sudden, sharp braking.
Q: Can I install a brake booster aftermarket?
A: Yes, you can install an aftermarket brake booster, but it’s essential to choose one that is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model. Additionally, seek professional installation to ensure it’s done correctly and safely.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, brake boosting is a valuable technique that can enhance your ability to stop safely in various situations. However, it should always be used responsibly and with an understanding of its potential risks. By following proper techniques, staying aware of your vehicle’s condition, and practicing safe driving habits, you can make the most of brake boosting while ensuring your safety and the safety of others on the road. Remember, responsible driving is the key to a safer and more enjoyable automotive experience. It is important to note that brake boosting is not a recommended technique for everyday driving. It should only be used in emergency situations or when necessary to maintain control of your vehicle.